
|
|
ADJUSTMENT, SHORT-RUN AGGREGATE MARKET: Disequilibrium in the short-run aggregate market induces changes in the price level that restore equilibrium. If the price level is above the short-run equilibrium price level, economy-wide product market surpluses cause the price level to fall. If the price level is below the short-run equilibrium price level, economy-wide product market shortages cause the price level to rise. In both cases short-run equilibrium is restored. You might want to compare adjustment, long-run aggregate market. Price level changes induce changes in both aggregate expenditures and real production. Unlike the long-run aggregate market, changes in the price level can induce changes in short-run aggregate supply, making it greater or less than full-employment real production.
Visit the GLOSS*arama
|
|


|

|
                           SELLERS' EXPECTATIONS, SUPPLY DETERMINANT: The expectations that sellers have concerning the future price of a good, which is assumed constant when a supply curve is constructed. If sellers expect a higher price, then supply decreases. If sellers expect a lower price, then supply increases. Sellers' expectations are one of five supply determinants that shift the supply curve when they change. The other four are resource prices, production technology, other prices, and number of sellers. The decision to sell a good today depends on expectations of future prices. Sellers seek to sell a good at the highest possible price. If they expect the price to rise in the future, they are inclined to sell less now. If sellers expect the price to decline in the future, they are inclined to sell more now.Looking to the FutureSellers make selling decisions based on a comparison of current and future prices. They are motivated to sell the good at the highest price possible. If that highest price is the one existing today, then they sell today. If that highest price is expected to occur in the future, then they wait until later to sell.Consider the example of Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos, a cute and cuddly line of stuffed creatures. Sellers decide how many Stuffed Amigos to sell, at a given current price, based on their expectations of future prices. - Price Going Higher: Suppose that news media throughout the country report on the prospects of a worldwide shortage of stuffing, the same sort of stuffing used to stuff Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos. Every expert interviewed projects that the higher stuffing prices will most assuredly cause an increase in the price of Stuffed Amigos. The price increase has not yet occurred, but it most assuredly will occur. Everyone expects it to occur. With this news, every store with Stuffed Amigos to sell is inclined to sell fewer today, holding off until the price rises. As such, the current supply decreases.
- Price Going Lower: Alternatively, suppose that The Wacky Willy Company, the firm that produces Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos announces that it has developed a new production technique, that when implemented will allow them to sell Stuffed Amigos at half their current price. This news is greeted with disdain by stores selling Stuffed Amigos. They expect that Stuffed Amigos will be sold at a lower price in the near future. With this news, every store is likely to sell as many Stuffed Amigos today as they can, at the higher price. As such, the current supply increases.
Shifting the Supply Curve| Sellers' Expectations | 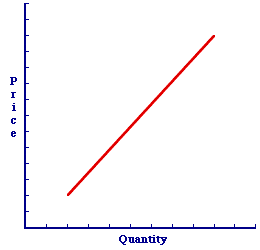 |
A change in sellers' expectations causes the supply curve to shift. This can be illustrated using the positively-sloped supply curve for Wacky Willy Stuffed Amigos presented in this exhibit. This supply curve captures the specific one-to-one, law of supply relation between supply price and quantity supplied. Sellers' expectations are assumed to remain constant with the construction of this supply curve.Now, consider how changes in sellers' expectations shift the supply curve. - Expecting Higher Prices: If sellers expect that the price of the good will be increasing in the future, then they are likely to sell less today. This causes a decrease in supply and a leftward shift of the supply curve. Click the [Expect Higher] button to demonstrate.
- Expecting Lower Prices: If sellers expect that the price of the good will be decreasing in the future, then they are likely to sell more today. This causes an increase in supply and a rightward shift of the supply curve. Click the [Expect Lower] button to demonstrate.
The Financial Power of ExpectationsSellers' expectations (especially when combined with buyers' expectations) play a critical role in the markets for numerous goods. At the very top of this list is the whole assortment of financial markets, especially the stock market. Those who buy and sell corporate stock do so largely based on expectations of future stock prices.For example, Winston Smythe Kennsington III, noted Shady Valley financial guru, might be inclined to sell his shares of OmniConglomerate, Inc. stock today if he expects that the price will fall below $50 in the future. Alternatively, he might be willing to buy a few thousand additional shares of OmniConglomerate, Inc. stock today if he expects that the price will exceed $50 in the future.

Recommended Citation:SELLERS' EXPECTATIONS, SUPPLY DETERMINANT, AmosWEB Encyclonomic WEB*pedia, http://www.AmosWEB.com, AmosWEB LLC, 2000-2024. [Accessed: May 1, 2024].
Check Out These Related Terms... | | | | | | |
Or For A Little Background... | | | | | | | | | | |
And For Further Study... | | | | | | |
Search Again?
Back to the WEB*pedia
|



|

|
PURPLE SMARPHIN
[What's This?]
Today, you are likely to spend a great deal of time at a garage sale wanting to buy either a birthday gift for your aunt or a pair of leather sandals that won't cause blisters. Be on the lookout for a thesaurus filled with typos.
Your Complete Scope
This isn't me! What am I?
|

|
|
Cyrus McCormick not only invented the reaper for harvesting grain, he also invented the installment payment for selling his reaper.
|

|
|
"It is part of the American character to consider nothing as desperate. " -- President Thomas Jefferson
|

|
CPI
Consumer Price Index
|

|
|
Tell us what you think about AmosWEB. Like what you see? Have suggestions for improvements? Let us know. Click the User Feedback link.
User Feedback
|


|


